Today is “Brain Injury Awareness Day” – Let’s talk about Brain Trauma and Depression
Every year, about 70 million people experience brain injuries, from concussions to more severe traumatic brain injuries (TBI). These injuries can have lasting effects on memory, mobility and overall well-being.
This day is dedicated to raising awareness, supporting survivors and advocating for better prevention and treatment. Whether through education, safety measures, or research, we can all play a role in reducing the impact of brain injuries.
While the immediate effects of TBI are well-known, the long-term psychological consequences, particularly the heightened risk of depression, are equally concerning.
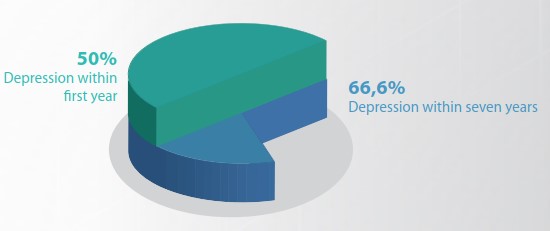
Research shows that 50% of TBI survivors develop depression within the first year, and up to 67% during their lifetime, much higher than the general population. This highlights the need for increased mental health support and pharmacological treatments for TBI patients.
Understanding the Link Between TBI and Depression
TBI can cause structural and chemical changes in the brain, affecting neurotransmitters like serotonin and dopamine, which regulate mood.
Inflammation and chronic neuroinflammation can also contribute to depression by impairing neural connections. Damage to brain regions such as the prefrontal cortex and limbic system, particularly in moderate to severe TBI cases, can lead to emotional instability and difficulty regulating emotions.
Furthermore, there is a strong correlation between specific neurotrophic factors, especially BDNF (Brain Derived Neurotrophic Factor), and depression and cognitive function.
Treatment and Management
Managing depression in TBI patients requires a comprehensive approach which makes longterm follow-up programs essential for patients.
Treatment options may include medication, such as antidepressants that target neurotransmitter imbalances, as well as psychotherapy, including cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT). Additionally, lifestyle modifications, physical rehabilitation, and social support can play crucial roles in improving mental health outcomes.
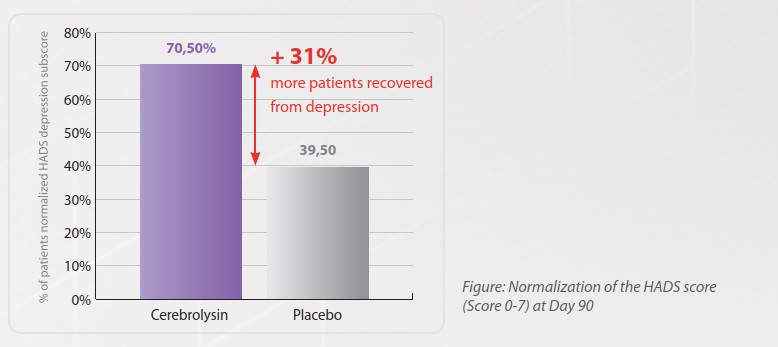
Cerebrolysin® has shown promising results in reducing depression following TBI due to its cerebroprotective and neurotrophic properties.
Its effectiveness is attributed to:
- Enhancement of Neurogenesis
- Reduction of Neuroinflammation
- Enhancement of Neurotransmitter Function
Conclusion
Cerebrolysin’s ability to support neuronal repair, reduce inflammation, enhance neurotransmitter function and prevent secondary brain injury makes it a valuable treatment for post-TBI depression. While more research is needed to establish standardized treatment protocols, its current clinical results indicate significant potential for improving mental health outcomes in TBI patients.
Read more about the effectivness of Cerebrolysin® in TBI (CAPTAIN study).